Key Takeaways
The rapid proliferation of IoT technology is fundamentally transforming how cities operate, manage resources, and respond to emerging challenges. As the next decade unfolds, smart cities are turning to connected devices not just to streamline operations, but to serve as foundational tools driving sustainability, adaptive infrastructure, and climate resilience. The following key trends and insights offer a holistic view of how IoT is poised to redefine urban living across multiple dimensions and industries:
- Adaptive infrastructure enables urban resilience: IoT-powered monitoring and real-time analytics allow infrastructure systems to dynamically adjust to environmental changes. This grants cities increased ability to prepare for and withstand climate events such as floods, heatwaves, and severe storms.
- Smarter resource allocation fuels sustainability: Connected sensors and data-driven technologies optimize the consumption and distribution of water, energy, and waste resources. These systems help ensure urban assets are used efficiently, directly reducing environmental impact while lowering operational costs.
- Environmental monitoring expands its role: Beyond regulatory compliance, continuous monitoring of air, water, and soil quality through IoT networks facilitates proactive interventions. Such capabilities directly support public health initiatives and broader urban sustainability goals.
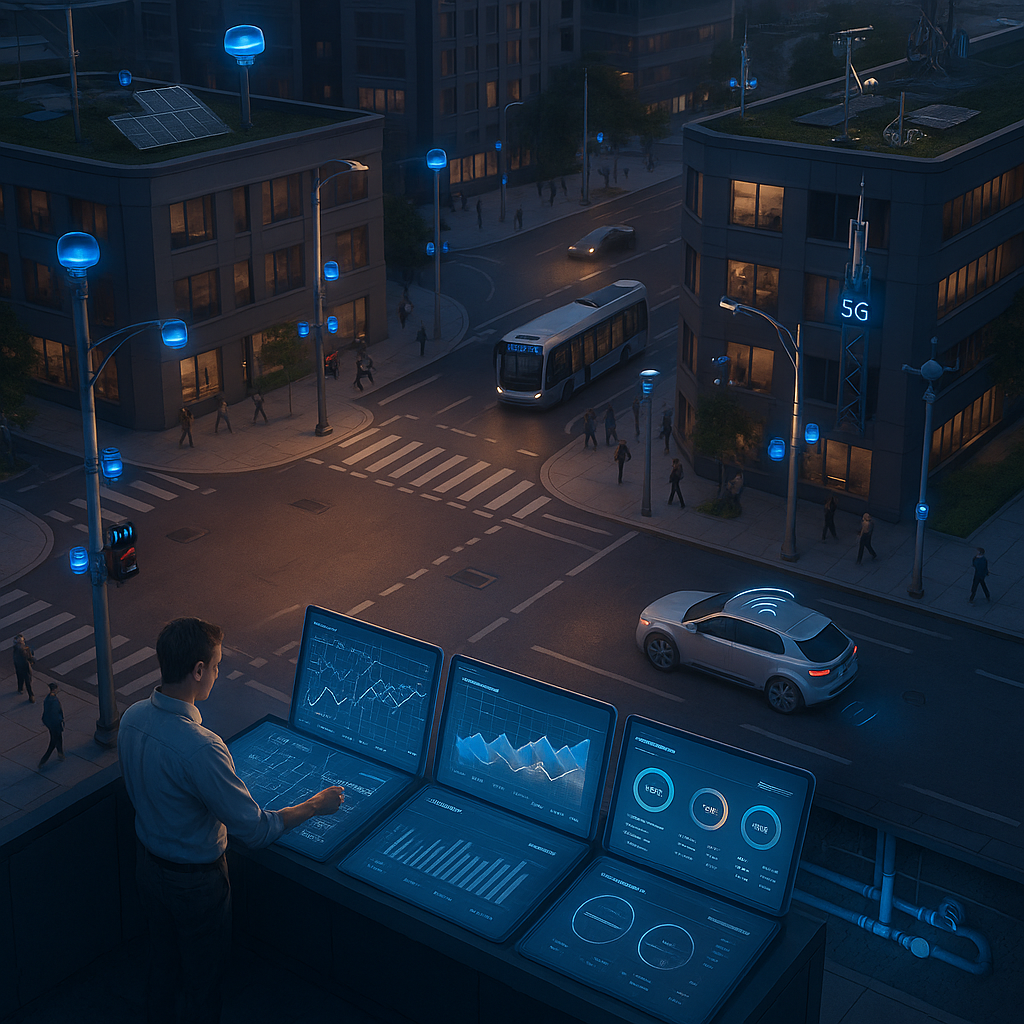
- 5G connectivity empowers advanced IoT deployments: With high-speed and low-latency 5G networks, cities can support massive numbers of connected devices and seamless real-time data flows. This is essential for the reliability of smart grids, autonomous mobility, and responsive emergency systems.
- Smart mobility solutions revolutionize urban transportation: IoT-enabled platforms integrate dynamic traffic management, public transit coordination, and last-mile logistics. As a result, cities experience reduced congestion, lower carbon emissions, and increased commuter satisfaction.
- Evolving security strategies protect digital infrastructure: The expansion of connected systems increases potential vulnerabilities, making comprehensive IoT security and privacy protocols critical. Protecting sensitive urban data is now essential for maintaining resident trust and system reliability.
- Technology and sustainability merge for climate adaptation: Advanced IoT applications are increasingly central to mitigating climate risks. Adaptive infrastructure, renewable resource integration, and predictive disaster management converge to make environmental stewardship a core of urban strategy.
As smart cities move from pilot projects to widescale adoption, it becomes crucial for city planners, technology leaders, and policymakers to fully understand these IoT trends. The following sections explore these shifts in depth, with diverse examples from healthcare, public safety, energy, logistics, and environmental management. This sets the stage for cities aspiring to be not only intelligent, but also resilient, inclusive, and sustainable.
Introduction
A decade ago, envisioning cities that could detect air quality, reroute traffic instantly, or precisely manage water consumption seemed far-fetched, relegated to science fiction. Today, these capabilities are becoming standard practice in leading urban centers, driven by an explosion in IoT-connected devices that form the digital backbone of modern smart cities. As adoption accelerates, cutting-edge IoT trends are redefining how municipalities anticipate challenges, share resources, and build resilience in the face of mounting environmental, economic, and societal pressures.
In this landscape, the integration of adaptive infrastructure, real-time resource management, and high-speed data connectivity is transforming not only how cities function but how they strategically plan for the future. This article examines the value of IoT across public administration, healthcare, finance, and beyond, highlighting the pivotal role of connected technology in shaping urban environments that are efficient, sustainable, and responsive to citizens’ evolving needs.
Un passo avanti. Sempre.
Unisciti al nostro canale Telegram per ricevere
aggiornamenti mirati, notizie selezionate e contenuti che fanno davvero la differenza.
Zero distrazioni, solo ciò che conta.
 Entra nel Canale
Entra nel Canale
IoT Infrastructure Evolution
Smart cities are built on robust and continually evolving IoT infrastructure. At the heart of this evolution is the rapid deployment of 5G networks, providing ultra-low latency and massive device connectivity. Today’s networks are capable of supporting up to one million connected devices per square kilometer, a tenfold increase over previous generations.
Modern IoT infrastructure typically comprises three layers: the perception layer (sensors and actuators), the network layer (for fast and reliable data transmission), and the application layer (where complex analysis and management occur). Around the world, cities like Barcelona have leveraged this model to great effect, achieving a 30% reduction in water consumption through smart meters and saving over $37 million annually via intelligent lighting systems.
Edge Computing Integration
While network evolution is crucial, the integration of edge computing marks a significant leap forward. By bringing processing power closer to data sources, edge devices dramatically reduce latency, up to 80% compared to cloud-only setups, while improving reliability. Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative, for example, processes traffic camera feeds in real time on the edge. This enables immediate responses to road incidents and has cut emergency response times by 20%.
Edge integration has broad applicability. In healthcare, it supports remote patient monitoring and instant anomaly detection; in manufacturing, it enables predictive maintenance on production lines; and in environmental science, it helps track and respond to sudden changes in air or water quality. Additionally, localized data processing reduces bandwidth costs by up to 30%, creating more resilient and cost-effective urban systems.
Climate Resilience Through Connected Infrastructure
With climate change presenting persistent risks, smart cities are deploying IoT networks to bolster resilience and protect communities. Environmental sensor arrays now provide real-time monitoring of air quality, temperature variations, and potential flood risks. These systems send vast streams of data for predictive modeling, which allows municipalities to respond proactively to emerging threats.
Adaptive Infrastructure Systems
Adaptive infrastructure takes this a step further, delivering responsive adjustments automatically based on environmental signals. Copenhagen, for instance, has established climate-adaptive neighborhoods that use IoT sensors to manage stormwater runoff. The system dynamically opens or closes drainage routes depending on rainfall intensity, cutting flood damage by 60% in impacted areas and saving the city an estimated $100 million in potential repair costs.
Beyond drainage, IoT-driven adaptive infrastructure also benefits healthcare and public safety. For example, automated systems can adjust HVAC operations in hospitals to manage air quality during wildfire events. Or they can reroute ambulance services in real time during citywide emergencies.
Resource Management Optimization
Optimizing resource management with IoT is revolutionizing municipal operations. Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) in smart grids captures highly detailed energy usage data, enabling dynamic balancing and demand-response programs. Municipalities implementing advanced metering see energy savings of 15-25% across public buildings.
Water and Waste Management
Innovation extends to water and waste management. In water distribution, connected sensors detect leaks with precision rates exceeding 95%, leading to reductions in water loss of up to 40%. Meanwhile, IoT-enabled waste bins equipped with fill-level sensors provide real-time status updates, allowing route optimization for collection vehicles. Amsterdam’s smart waste management system cuts fuel consumption by 30%, trims operational costs by 25%, and has reduced emissions by 20%.
Industries beyond public works are embracing similar principles. In hospitality, connected systems streamline housekeeping schedules and energy use. In education, water and power consumption can be automatically managed based on occupancy, lowering utility costs while also supporting sustainability.
Smart Mobility Solutions
The transportation sector stands at the forefront of IoT-driven transformation. AI-powered traffic management systems are now widely deployed, utilizing cameras and connected sensors to analyze vehicle movement and adjust traffic flows dynamically. Major corridors adopting these systems report congestion reductions of 20-30% and transit time improvements from 15-25%.
Connected Vehicle Infrastructure
The advent of Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) technology marks another leap in urban mobility. Columbus, Ohio, implemented a connected vehicle system that lowered intersection crash rates by 40% and improved emergency vehicle response times by 25%. These solutions prioritize ambulances and first responders at traffic signals and optimize public transit operations, boosting overall citywide efficiency.
Other sectors also benefit from IoT mobility integration. In logistics, real-time tracking optimizes last-mile delivery, reducing costs and environmental impact. Retailers leverage location data to offer dynamic pickup or delivery options, improving customer satisfaction and operational agility.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Expanding IoT connectivity brings increased security and privacy challenges. With studies indicating over half of IoT devices are vulnerable to medium or high-severity attacks, cities face growing pressure to safeguard digital assets and resident data.
Smart cities are adopting layered security approaches, utilizing blockchain technology for secure, auditable data transmission and implementing zero-trust architectures to verify every device interacting with municipal systems. These frameworks are becoming standard not only in government deployments but also in healthcare, finance, and retail, where sensitive data flows require bulletproof protection.
Data Protection Frameworks
Comprehensive data privacy frameworks are essential for public trust and regulatory compliance. These frameworks often include end-to-end encryption, regular security audits, and tightly controlled access permissions. Toronto’s smart city projects exemplify these best practices by embedding privacy-by-design principles from inception and establishing transparent data governance policies that empower citizens with both information and control.
Un passo avanti. Sempre.
Unisciti al nostro canale Telegram per ricevere
aggiornamenti mirati, notizie selezionate e contenuti che fanno davvero la differenza.
Zero distrazioni, solo ciò che conta.
 Entra nel Canale
Entra nel Canale
Financial institutions, educational systems, and healthcare providers are following suit, building privacy protections into every phase of connected technology adoption to ensure robust defense against evolving cyber threats.
Future Technology Integration
Looking ahead, the next chapter of smart city evolution will be characterized by deep integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cutting-edge sensor technology. Advanced neural networks are increasingly deployed to analyze cross-system patterns, unlocking predictive maintenance capabilities that reduce infrastructure failures by as much as 50%.
Emerging Technologies
Quantum sensors and advanced materials promise to boost the sensitivity and durability of IoT devices, slashing power requirements by up to 90%. Seoul leads in piloting quantum-secured communication networks that shield critical municipal infrastructure from even the most sophisticated cyber threats. In healthcare, quantum-enhanced sensors may soon enable real-time monitoring and early detection of pathogens, further underscoring the breadth of IoT’s transformative impact.
Retailers prepare for ultra-personalized customer engagement through AI-driven in-store experiences, while environmental agencies harness quantum precision to track micro-pollutants and assess climate interventions in real time. The convergence of these innovations points toward highly adaptive, secure, and intelligent urban environments across every domain.
Conclusion
IoT infrastructure is ushering in a new era for urban environments, translating the smart city concept from vision to everyday reality. Through the strategic integration of 5G connectivity, edge computing, and intelligent sensor networks, cities are achieving heightened levels of efficiency, adaptability, and resilience. This impacts everything from energy grids and healthcare facilities to mobility solutions and emergency services. The insights and optimizations generated by these systems are creating tangible benefits: lower energy and resource waste, reduced emissions, and enhanced public safety, to name a few.
Yet, greater connectivity necessitates unwavering attention to security and privacy. The rise of multi-layered defense architectures and citizen-centric data governance is a sign of increased maturity in how cities, along with private sector partners, manage risk while building public confidence.
As we look toward the future, accelerating advances in AI and quantum technologies are set to make urban landscapes even more responsive, secure, and sustainable. For city leaders, technologists, and everyday citizens alike, the opportunity lies in moving beyond merely responding to change. The real competitive advantage will go to those who proactively shape it: anticipating needs, adopting adaptive technologies, and reimagining how connected innovation can empower every aspect of urban life. The question is not if cities will harness these advancements, but how they will use them to build resilient, future-proof communities poised to thrive in a rapidly changing world.




Leave a Reply