Key Takeaways
- Malware is being distributed by hackers posing as WhatsApp and TikTok, two of the world’s most widely downloaded social platforms.
- The threat targets Android devices globally, with detections in app stores serving users across multiple countries.
- Once installed, the malware can access contacts, messages, and private accounts, putting sensitive user data at risk.
- Most infections occur when users download apps from third-party sites rather than the official Google Play Store.
- Google and cybersecurity firms are investigating the spread. Google Play is increasing warnings and detection for suspicious apps.
- Experts urge users to download only from trusted sources and to keep Android security patches updated.
Introduction
A recent surge in Android malware is putting users at risk across the globe by disguising itself as trusted apps such as WhatsApp and TikTok, according to cybersecurity experts. The malware has been detected both on app stores and third-party sites, luring users into downloading it and putting personal data and device security in jeopardy. Security teams recommend extra vigilance, including downloading only official versions and keeping devices updated.
How the Malware Operates
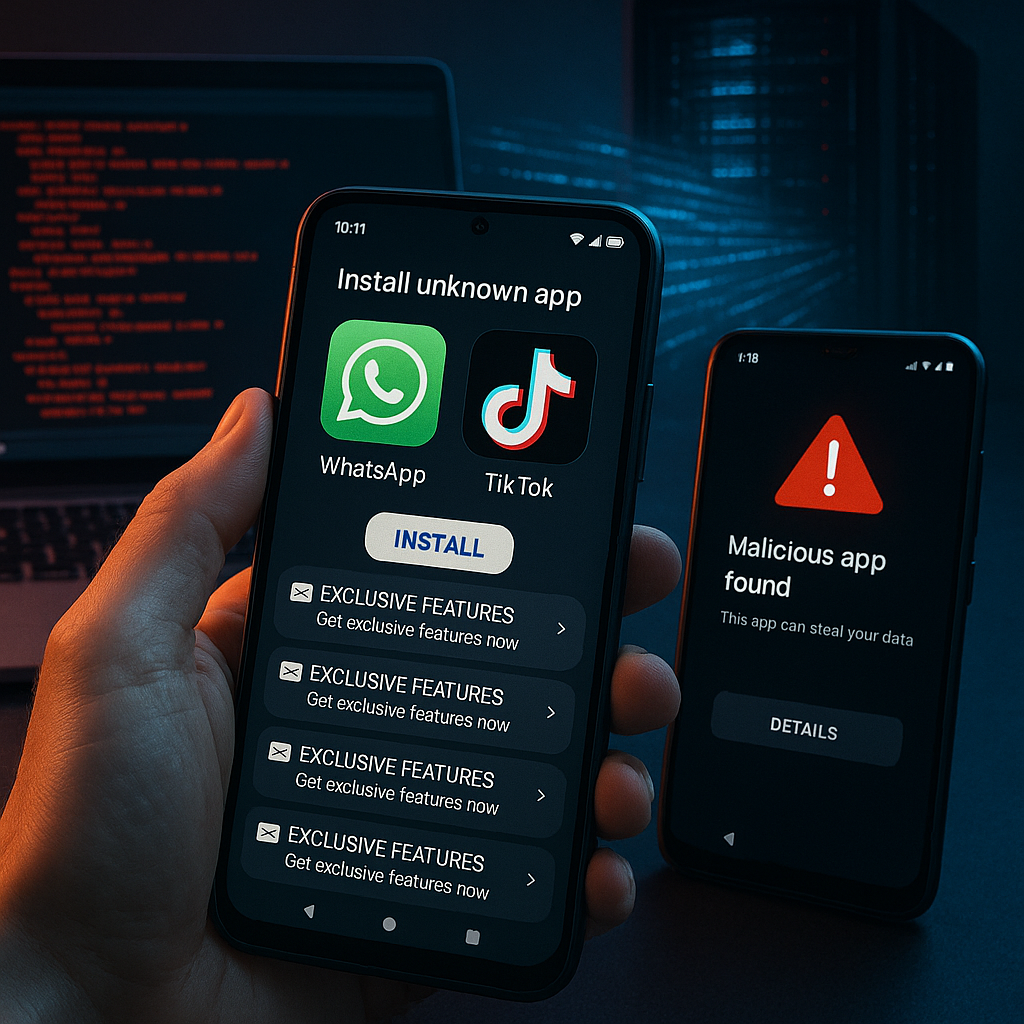
Researchers at CheckPoint identified more than 50,000 downloads of malicious apps masquerading as WhatsApp and TikTok on third-party Android app stores this month. This malware, called “SocialStealer,” closely replicates the appearance and login processes of legitimate versions.
After installation, the malware requests extensive permissions such as access to contacts, SMS messages, and administrative functions. Maria Chen, lead researcher at CheckPoint, stated that SocialStealer is “particularly sophisticated in how it maintains a functioning front-end while secretly harvesting data in the background.”
Fake apps may display working message interfaces and video feeds drawn from web sources, convincingly imitating genuine apps. However, credentials and other personal data entered by users are transmitted to command servers primarily based in Eastern Europe.
Un passo avanti. Sempre.
Unisciti al nostro canale Telegram per ricevere
aggiornamenti mirati, notizie selezionate e contenuti che fanno davvero la differenza.
Zero distrazioni, solo ciò che conta.
 Entra nel Canale
Entra nel Canale
Infection Methods and Spread
This malware spreads mainly through phishing messages and misleading ads that offer “exclusive features” or “early access” to new app functionalities. Recipients often receive these through SMS, WhatsApp, or email.
Researchers have also detected it spreading via search engine ads promoting “premium” or “plus” versions of well-known social apps. Google has removed several campaigns designed to direct users to third-party stores hosting infected versions.
While initial outbreaks focused on users in Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe, researchers have noticed growing infection attempts in North America and Western Europe over the past two weeks.
Warning Signs and Detection
The most reliable warning sign of a fake app is its source of installation. Genuine WhatsApp and TikTok apps are available only on the official Google Play Store or Apple App Store.
Other signs include:
- Requests for unusual device permissions during installation
- Features or offers that appear too good to be true
- Slight differences in app names or logos compared to the real application
- Pop-ups requesting login credentials shortly after setup
- Unexpected battery drain or device performance slowdown
For a comprehensive checklist on staying secure, see our guide on daily cyber hygiene habits.
Protection and Removal Steps
Users should check for unauthorized applications on their devices and ensure WhatsApp and TikTok are installed from official sources. Jake Sullivan, mobile security analyst at Kaspersky, emphasized that “the first line of defense is always the app store source.”
To reduce risk:
- Download apps only from official stores
- Enable Google Play Protect on Android devices
- Review app permissions before granting access
- Keep operating systems up to date
- Consider installing a reputable mobile security solution
You can also compare trusted antivirus apps for mobile security to safeguard your device against threats.
If infection is suspected, removing the malware requires extra steps. Maria Chen warned that simply uninstalling the app may not be sufficient. Users should first revoke any device admin privileges granted to the malicious app, then perform a full security scan.
Practical insights on how to recognize phishing messages—one of the common infection methods—can be found in these phishing email tips for online safety.
Conclusion
The spread of SocialStealer malware underscores how convincingly fake apps and deceptive campaigns can compromise Android device security. With evolving threats, users must remain alert to app sources and permission requests. What to watch: Cybersecurity experts continue to monitor infection patterns and expect further guidance as this malware variant develops.
For more information about identifying fake apps, see the 2025 scam alert and fake app warning signs.



Leave a Reply