Key Takeaways
- Malware disguised in GitHub projects: Threat actors have uploaded malicious code to repositories with appealing project names designed to attract unsuspecting developers.
- SEO manipulation increases reach: Attackers use search engine optimization to boost their projects’ visibility, making it more likely for developers to encounter infected repositories during routine searches.
- Developers and open-source projects at risk: The campaign targets professionals looking for trending libraries or quick solutions, placing user data and business operations in danger.
- Exposure could lead to wider supply chain attacks: Once installed, the malware can access credentials and propagate through connected systems. This amplifies its potential impact across organizations.
- Cybersecurity firms urge heightened vigilance: Security experts recommend developers vet repositories carefully, double-check package sources, and rely on trusted recommendations to avoid infection.
- Further advisories and security patches expected: Security vendors are monitoring the situation and may release updated tools or advisories as more technical details emerge.
Introduction
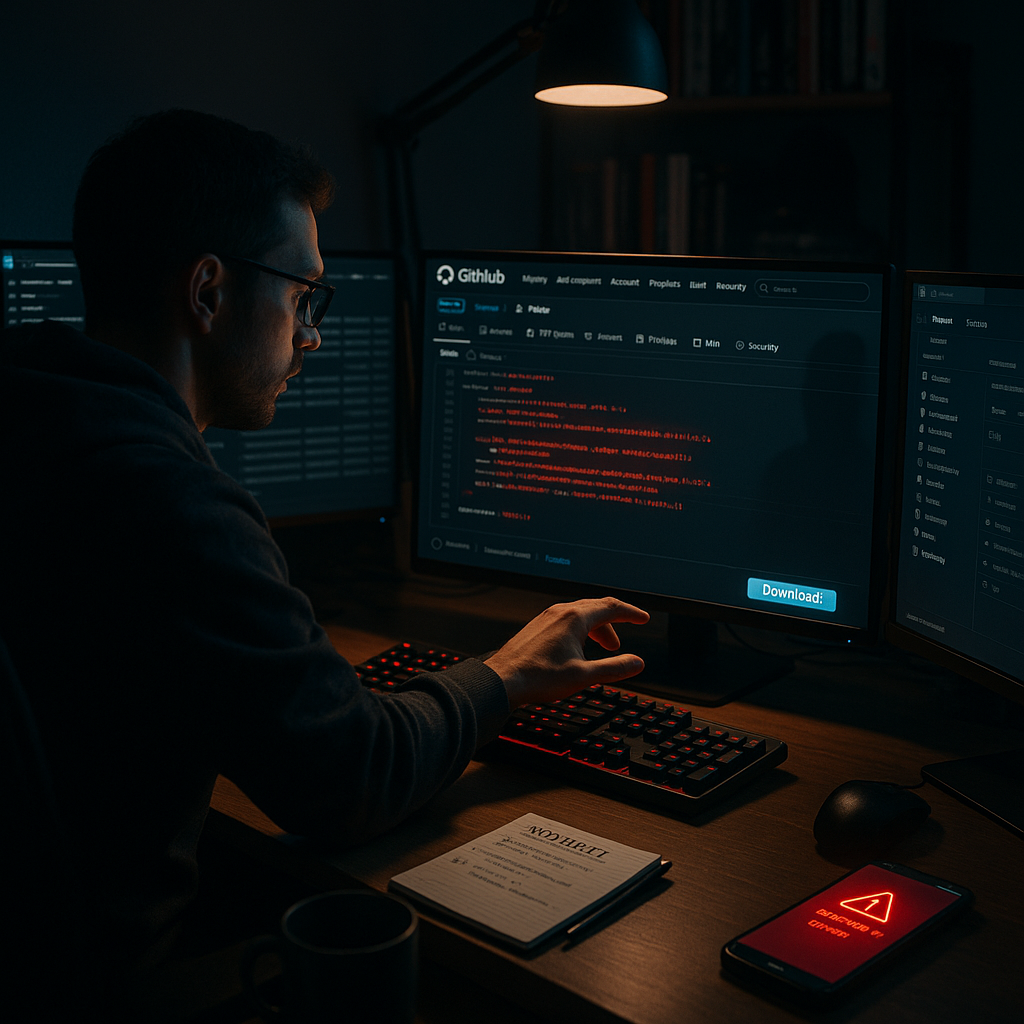
A newly identified Chinese malware campaign is targeting developers worldwide by spreading disguised malicious code through seemingly legitimate GitHub repositories, cybersecurity researchers reported this week. By manipulating search engine rankings, attackers are directing tech professionals to infected projects, raising concerns about compromised data and potential supply chain risks for open-source software. Security experts urge extra vigilance as advisories and protections are updated.
How the Malware Campaign Works
Security researchers at CyberDefend have uncovered a sophisticated Chinese malware operation that exploits GitHub’s search rankings to target developers. The attackers create repositories with names and descriptions that mimic popular development tools, embedding malicious code within seemingly legitimate package files.
These malicious repositories use search engine optimization techniques to appear at the top of GitHub search results. Dr. Sarah Chen, lead researcher at CyberDefend, explained that the threat actors have carefully studied developer search patterns and optimized their fake repositories to match common queries.
The malware is activated when developers incorporate the compromised packages into their projects. Once executed, it establishes persistent access to the infected system and can harvest credentials, API keys, and other sensitive development assets.
Un passo avanti. Sempre.
Unisciti al nostro canale Telegram per ricevere
aggiornamenti mirati, notizie selezionate e contenuti che fanno davvero la differenza.
Zero distrazioni, solo ciò che conta.
 Entra nel Canale
Entra nel Canale
Infection Method and Spread
The primary infection vector relies on developers searching for quick solutions to common coding problems. Developers under time pressure may skip thorough verification when they find these malicious packages, as the repositories often appear legitimate.
Attackers enhance credibility with elaborate documentation and readme files. The repositories maintain active commit histories and include genuine code samples alongside the malicious components.
Investigations reveal that over 300 compromised packages have been identified since January, with many remaining undetected for weeks or months. The malware particularly targets developers working with Python, JavaScript, and Ruby packages.
Detection and Impact
Security teams have observed the malware operating across multiple continents, with significant concentrations in North America and Europe. The campaign has already affected several thousand developers and potentially compromised numerous development pipelines.
The malware employs sophisticated detection evasion techniques, making it especially challenging to identify. Mark Rodriguez, chief security analyst at CodeGuard, stated that the campaign shows an unprecedented level of social engineering combined with technical sophistication.
Affected organizations have reported that the malware accessed sensitive development environments, potentially exposing proprietary code. Several major technology companies have initiated security audits after discovering compromised packages in their systems.
Protection Measures
Developers should take several immediate protective steps when working with GitHub repositories:
- Verify package authenticity through multiple sources.
- Check repository age and contributor histories.
- Review permission requests carefully during installation.
- Use automated security scanning tools for all third-party code.
Organizations are advised to update their security policies regarding open-source package usage. Jennifer Park, director of security at the Open Source Security Foundation, noted that implementing strict code review processes and maintaining approved package lists can significantly reduce risk exposure.
The GitHub security team has deployed enhanced detection mechanisms to identify suspicious repository patterns. They recommend enabling two-factor authentication and using signed commits to verify code authenticity.
Conclusion
The discovery of this GitHub malware campaign highlights growing risks for developers who rely on open-source code. Attackers are increasingly blending social engineering with technical manipulations, challenging established security practices. Enhanced security measures and vigilant review are becoming essential industry responses to these evolving threats. What to watch: updates from GitHub on detection efforts and any new security guidelines released for open-source contributors.




Leave a Reply