Key Takeaways
- Attackers are using SEO tactics to boost malicious GitHub repositories in search results, increasing the risk of developer downloads.
- This campaign specifically targets developers seeking open-source scripts or tools, rather than typical end-users.
- Researchers have linked the operation to actors associated with Chinese cyber-espionage campaigns.
- Compromised developer machines put downstream software projects and client security at risk.
- GitHub and cybersecurity firms urge enhanced repository vetting and increased vigilance for suspicious code.
- Researchers recommend ongoing monitoring, warning that this attack vector could evolve further.
Introduction
A wave of GitHub SEO poisoning attacks, disclosed by cybersecurity researchers in early June 2024, is placing developers and the broader software supply chain at risk. Chinese-linked malware campaigns are manipulating search results to entice users into downloading malicious code from compromised repositories. This threat focuses on those searching for open-source tools, prompting experts and GitHub to call for enhanced caution and ongoing monitoring.
Attack Methodology and Detection
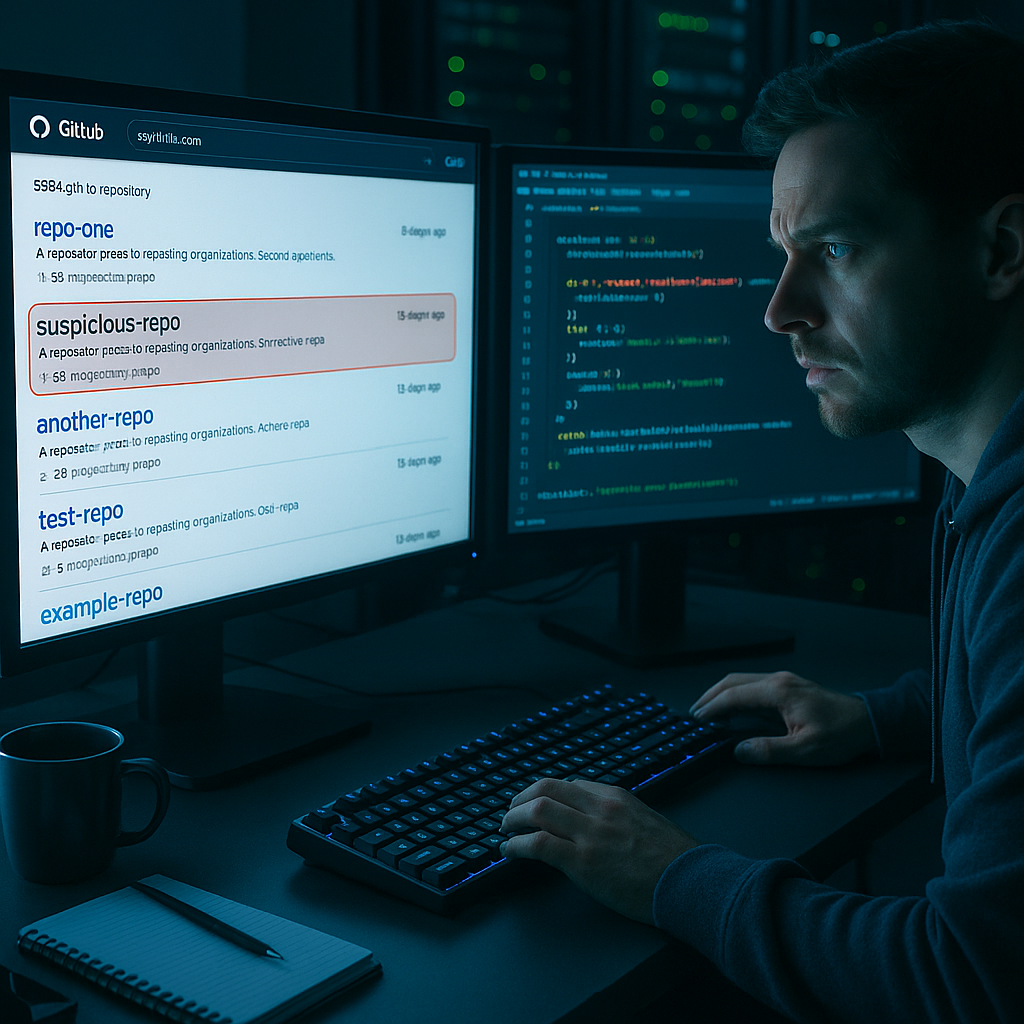
Chinese threat actors have used search engine optimization to elevate malicious GitHub repositories in search results. Multiple cybersecurity firms report that attackers create convincing repository copies that appear prominently when developers look for coding solutions or open-source tools.
Researchers found these repositories contain code that looks legitimate but hides malware including HiddenGh0st, Winos, and kkRAT. These malicious packages run automatically when downloaded and compiled on developer systems.
The attackers exploit developers’ preference for general search engines over GitHub’s internal search. By carefully crafting repository names, descriptions, and documentation to replicate popular legitimate projects, malicious actors make these repositories difficult to distinguish at first glance.
Un passo avanti. Sempre.
Unisciti al nostro canale Telegram per ricevere
aggiornamenti mirati, notizie selezionate e contenuti che fanno davvero la differenza.
Zero distrazioni, solo ciò che conta.
 Entra nel Canale
Entra nel Canale
Target Profile and Impact
Software developers and their teams are the main targets of these GitHub SEO poisoning attacks, marking a significant shift from traditional end-user-focused threats. The campaign exploits the trust developers have in the open-source community and the way they typically work.
Infected developer machines can provide attackers with access to the wider software supply chain. Security analysts highlight that compromised development environments could lead to unintentional malware distribution through software updates and dependencies.
Organizations using GitHub-sourced components face measurable risks if developers unknowingly download compromised packages. The consequences extend beyond individual developers and can affect downstream software projects and end-users. For steps organizations and individuals can take to strengthen their online safety practices, see this cyber hygiene checklist.
Threat Actor Analysis
Researchers attribute these campaigns to advanced Chinese malware operations based on the infrastructure and malware features observed. The responsible groups show deep understanding of developer workflows and software supply chain dynamics.
Attackers have focused on repositories connected to popular development frameworks and frequently searched coding solutions. Their tactics reflect careful target selection and long-term planning.
Analysis of the malware, especially the HiddenGh0st variant, reveals sophisticated methods for maintaining system persistence and evading detection. This variant includes features designed to bypass common security controls in development environments.
Security Risks and Implications
This campaign represents an escalation in software supply chain threats. Unlike more common malware distribution vectors, these attacks directly target development at its source.
Compromised development environments can result in infected software builds, posing risks to thousands of users further down the chain. Experts caution that detecting such compromises is challenging once malicious code is integrated into otherwise legitimate projects.
The success of these attacks in bypassing typical security measures exposes key vulnerabilities in how developers discover and adopt open-source code. Organizations must balance the need for development efficiency with stronger security controls. To explore how habits and proactive routines can reduce risk, review these trusted antivirus apps that can help detect such threats early.
Mitigation Strategies
Security experts recommend that organizations adopt strict verification steps for open-source components. This includes relying on GitHub’s native search functions and activating features such as dependency scanning and two-factor authentication.
Developers should confirm repository legitimacy by reviewing contributor history, star counts, and recent activity. Security teams stress the necessity of code review processes that include malware scanning before code integration.
Clear policies for third-party code usage and automated detection tools are advised to spot potential threats. Ongoing security training should address the unique risks presented by SEO poisoning campaigns. Utilize basic principles of two-factor authentication to further enhance developer account protection.
Future Outlook
Security researchers anticipate that similar attacks will increase as threat actors continue to target software supply chains. The effectiveness of these GitHub SEO poisoning attacks may motivate the emergence of new variants aimed at other developer platforms.
Platform providers and security firms are improving detection tools designed to identify repository-based threats. These efforts focus on more sophisticated automated scanning and stronger verification mechanisms for open-source code.
The development community will continue to face challenges balancing collaborative open-source practices with increasing security demands. Industry specialists reinforce the need for better security awareness and tools purpose-built for protecting the software development process. For foundational advice on everyday security, see the password manager guide.
Conclusion
The GitHub SEO poisoning campaign highlights how attackers are now directly targeting software developers, taking advantage of trusted workflows to distribute advanced Chinese malware. This development reveals broader vulnerabilities across the software supply chain, putting downstream users and projects at risk. What to watch: cybersecurity providers are enhancing automated tools and detection methods to identify and stop repository-based threats in real time. For more practical tips and daily routines to improve your preparedness, explore this cyber hygiene checklist.
Un passo avanti. Sempre.
Unisciti al nostro canale Telegram per ricevere
aggiornamenti mirati, notizie selezionate e contenuti che fanno davvero la differenza.
Zero distrazioni, solo ciò che conta.
 Entra nel Canale
Entra nel Canale



Leave a Reply